69 Harriet Beecher Stowe’s “Trials of a Housekeeper”

In This Chapter
Author Background
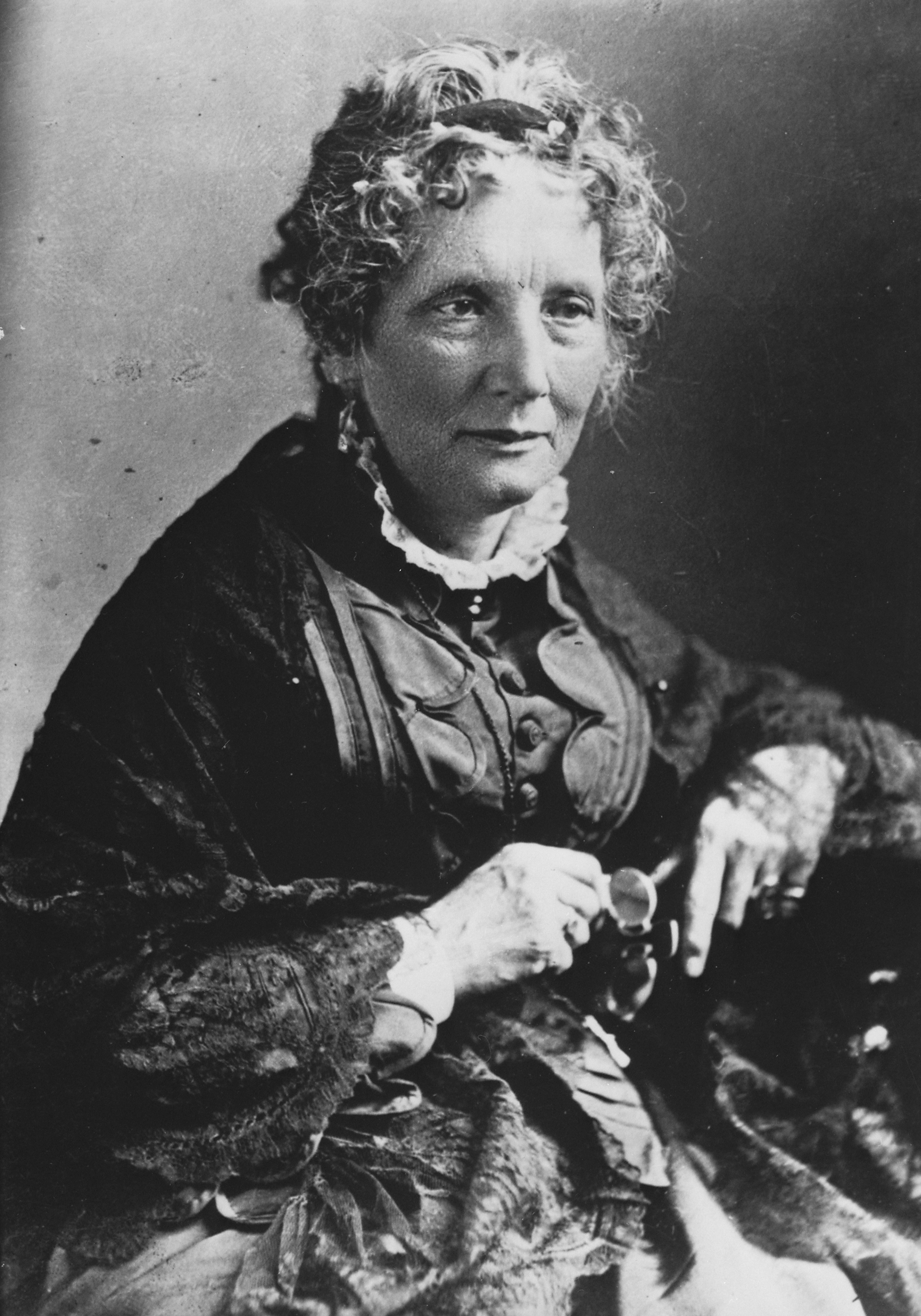
Harriet Beecher Stowe (1811-1896) was an American author and abolitionist best known for her novel Uncle Tom’s Cabin, which played a significant role in shaping public opinion on slavery in the United States. Born in Litchfield, Connecticut, Stowe came from a prominent family of religious and intellectual background. Her father, Lyman Beecher, was a renowned Congregationalist minister, and her siblings were involved in various intellectual pursuits.
Stowe’s early exposure to her father’s sermons and discussions about slavery instilled in her a deep sense of justice and moral responsibility. In 1832, she moved to Cincinnati, Ohio, after her marriage to Calvin Ellis Stowe, a biblical scholar and educator. It was in Ohio that Stowe witnessed firsthand the harsh realities of slavery, as Cincinnati served as a key stop on the Underground Railroad.

In 1851, Stowe’s serialized novel Uncle Tom’s Cabin was published. The novel depicted the brutalities and injustices faced by enslaved African Americans and was immensely popular, selling millions of copies and fueling abolitionist sentiments. Uncle Tom’s Cabin contributed to the anti-slavery movement and is credited with helping to lay the groundwork for the American Civil War.
Beyond her work as an abolitionist, Stowe wrote extensively on various social and political issues of her time. She penned novels, essays, and articles on women’s rights, temperance, and education. Stowe’s writing often reflected her strong moral convictions and her desire to effect social change.
In addition to her literary achievements, Stowe was an active supporter of the women’s suffrage movement and advocated for women’s rights. She used her platform as a writer and speaker to address issues of gender inequality and advocate for women’s education and empowerment.
Harriet Beecher Stowe’s impact on American literature and the abolitionist movement cannot be overstated. Her writings helped raise awareness about the horrors of slavery, challenged societal norms, and promoted the cause of equality. Stowe’s work continues to be studied and celebrated for its influence on American history and its contribution to the fight for social justice.
TRIALS OF A HOUSEKEEPER (1839)
Written by: Harriet Beecher Stowe
Copyright: Public Domain
I have a detail of very homely grievances to present; but such as they are, many a heart will feel them to be heavy—the trials of a housekeeper.
“Poh!” says one of the lords of creation, taking his cigar out of his mouth, and twirling it between his two first fingers, “what a fuss these women do make of this simple matter of managing a family! I can’t see for my life as there is anything so extraordinary to be done in this matter of housekeeping: only three meals a day to be got and cleared off—and it really seems to take up the whole of their mind from morning till night. I could keep house without so much of a flurry, I know.”
Now, prithee, good brother, listen to my story, and see how much you know about it. I came to this enlightened West about a year since, and was duly established in a comfortable country residence within a mile and a half of the city, and there commenced the enjoyment of domestic felicity. I had been married about three months, and had been, previously in love in the most approved romantic way, with all the proprieties of moonlight walks, serenades, sentimental billets doux, and everlasting attachment.
After having been allowed, as I said, about three months to get over this sort of thing, and to prepare for realities, I was located for life as aforesaid. My family consisted of myself and husband, a female friend as a visitor, and two brothers of my good man, who were engaged with him in business.
I pass over the first two or three days, spent in that process of hammering boxes, breaking crockery, knocking things down and picking them up again, which is commonly called getting to housekeeping. As usual, carpets were sewed and stretched, laid down, and taken up to be sewed over; things were formed, and reformed, transformed, and conformed, till at last a settled order began to appear. But now came up the great point of all. During our confusion we had cooked and eaten our meals in a very miscellaneous and pastoral manner, eating now from the top of a barrel, and now from a fireboard laid on two chairs, and drinking, some from teacups, and some from saucers, and some from tumblers, and some from a pitcher big enough to be drowned in, and sleeping, some on sofas, and some on straggling beds and mattresses thrown down here and there wherever there was room. All these pleasant barbarities were now at an end. The house was in order, the dishes put up in their places; three regular meals were to be administered in one day, all in an orderly, civilized form; beds were to be made, rooms swept and dusted, dishes washed, knives scoured, and all the et cetera to be attended to. Now for getting “help,” as Mrs. Trollope says; and where and how were we to get it? We knew very few persons in the city; and how were we to accomplish the matter? At length the “house of employment” was mentioned; and my husband was dispatched thither regularly every day for a week, while I, in the mean time, was very nearly dispatched by the abundance of work at home. At length, one evening, as I was sitting completely exhausted, thinking of resorting to the last feminine expedient for supporting life, viz., a good fit of crying, my husband made his appearance, with a most triumphant air, at the door. “There, Margaret, I have got you a couple at last—cook and chambermaid.” So saying, he flourished open the door, and gave to my view the picture of a little, dry, snuffy-looking old woman, and a great, staring Dutch girl, in a green bonnet with red ribbons, with mouth wide open, and hands and feet that would have made a Greek sculptor open his mouth too. I addressed forthwith a few words of encouragement to each of this cultivated-looking couple, and proceeded to ask their names; and forthwith the old woman began to snuffle and to wipe her face with what was left of an old silk pocket-handkerchief preparatory to speaking, while the young lady opened her mouth wider, and looked around with a frightened air, as if meditating an escape. After some preliminaries, however, I found out that my old woman was Mrs. Tibbins, and my Hebe’s name was Kotterin; also, that she knew much more Dutch than English, and not any too much of either. The old lady was the cook. I ventured a few inquiries. “Had she ever cooked?”
“Yes, ma’am, sartain; she had lived at two or three places in the city.”
“I suspect, my dear,” said my husband confidently, “that she is an experienced cook, and so your troubles are over;” and he went to reading his newspaper. I said no more, but determined to wait till morning. The breakfast, to be sure, did not do much honor to the talents of my official; but it was the first time, and the place was new to her. After breakfast was cleared away I proceeded to give directions for dinner; it was merely a plain joint of meat, I said, to be roasted in the tin oven. The experienced cook looked at me with a stare of entire vacuity. “The tin oven,” I repeated, “stands there,” pointing to it.
She walked up to it, and touched it with such an appearance of suspicion as if it had been an electrical battery, and then looked round at me with a look of such helpless ignorance that my soul was moved. “I never see one of them things before,” said she.
“Never saw a tin oven!” I exclaimed. “I thought you said you had cooked in two or three families.”
“They does not have such things as them, though,” rejoined my old lady. Nothing was to be done, of course, but to instruct her into the philosophy of the case; and having spitted the joint, and given numberless directions, I walked off to my room to superintend the operations of Kotterin, to whom I had committed the making of my bed and the sweeping of my room, it never having come into my head that there could be a wrong way of making a bed; and to this day it is a marvel to me how any one could arrange pillows and quilts to make such a nondescript appearance as mine now presented. One glance showed me that Kotterin also was “just caught,” and that I had as much to do in her department as in that of my old lady.
Just then the doorbell rang. “Oh, there is the doorbell,” I exclaimed. “Run, Kotterin, and show them into the parlor.”
Kotterin started to run, as directed, and then stopped, and stood looking round on all the doors and on me with a wofully puzzled air. “The street door,” said I, pointing towards the entry. Kotterin blundered into the entry, and stood gazing with a look of stupid wonder at the bell ringing without hands, while I went to the door and let in the company before she could be fairly made to understand the connection between the ringing and the phenomenon of admission.
As dinner time approached, I sent word into my kitchen to have it set on; but recollecting the state of the heads of department there, I soon followed my own orders. I found the tin oven standing out in the middle of the kitchen, and my cook seated à la Turc in front of it, contemplating the roast meat with full as puzzled an air as in the morning. I once more explained the mystery of taking it off, and assisted her to get it on to the platter, though somewhat cooled by having been so long set out for inspection. I was standing holding the spit in my hands, when Kotterin, who had heard the doorbell ring, and was determined this time to be in season, ran into the hall, and, soon returning, opened the kitchen door, and politely ushered in three or four fashionable looking ladies, exclaiming, “Here she is.” As these were strangers from the city, who had come to make their first call, this introduction was far from proving an eligible one—the look of thunderstruck astonishment with which I greeted their first appearance, as I stood brandishing the spit, and the terrified snuffling and staring of poor Mrs. Tibbins, who again had recourse to her old pocket-handkerchief, almost entirely vanquished their gravity, and it was evident that they were on the point of a broad laugh; so, recovering my self-possession, I apologized, and led the way to the parlor.
Let these few incidents be a specimen of the four mortal weeks that I spent with these “helps,” during which time I did almost as much work, with twice as much anxiety, as when there was nobody there; and yet everything went wrong besides. The young gentlemen complained of the patches of starch grimed to their collars, and the streaks of black coal ironed into their dickies, while one week every pocket-handkerchief in the house was starched so stiff that you might as well have carried an earthen plate in your pocket; the tumblers looked muddy; the plates were never washed clean or wiped dry unless I attended to each one; and as to eating and drinking, we experienced a variety that we had not before considered possible.
At length the old woman vanished from the stage, and was succeeded by a knowing, active, capable damsel, with a temper like a steel-trap, who remained with me just one week, and then went off in a fit of spite. To her succeeded a rosy, good-natured, merry lass, who broke the crockery, burned the dinner, tore the clothes in ironing, and knocked down everything that stood in her way about the house, without at all discomposing herself about the matter. One night she took the stopper from a barrel of molasses, and came singing off upstairs, while the molasses ran soberly out into the cellar bottom all night, till by morning it was in a state of universal emancipation. Having done this, and also dispatched an entire set of tea things by letting the waiter fall, she one day made her disappearance.
Then, for a wonder, there fell to my lot a tidy, efficient, trained English girl; pretty, and genteel, and neat, and knowing how to do everything, and with the sweetest temper in the world. “Now,” said I to myself, “I shall rest from my labors.” Everything about the house began to go right, and looked as clean and genteel as Mary’s own pretty self. But, alas! this period of repose was interrupted by the vision of a clever, trim-looking young man, who for some weeks could be heard scraping his boots at the kitchen door every Sunday night; and at last Miss Mary, with some smiling and blushing, gave me to understand that she must leave in two weeks.
“Why, Mary,” said I, feeling a little mischievous, “don’t you like the place?”
“Oh, yes, ma’am.”
“Then why do you look for another?”
“I am not going to another place.”
“What, Mary, are you going to learn a trade?”
“No, ma’am.”
“Why, then, what do you mean to do?”
“I expect to keep house myself, ma’am,” said she, laughing and blushing.
“Oh ho!” said I, “that is it;” and so in two weeks I lost the best little girl in the world: peace to her memory.
After this came an interregnum, which put me in mind of the chapter in Chronicles that I used to read with great delight when a child, where Basha, and Elah, and Tibni, and Zimri, and Omri, one after the other, came on to the throne of Israel, all in the compass of half a dozen verses. We had one old woman, who stayed a week, and went away with the misery in her tooth; one young woman, who ran away and got married; one cook, who came at night and went off before light in the morning; one very clever girl, who stayed a month, and then went away because her mother was sick; another, who stayed six weeks, and was taken with the fever herself; and during all this time, who can speak the damage and destruction wrought in the domestic paraphernalia by passing through these multiplied hands?
What shall we do? Shall we give up houses, have no furniture to take care of, keep merely a bag of meal, a porridge pot, and a pudding stick, and sit in our tent door in real patriarchal independence? What shall we do?
The following discussion questions aim to delve into the themes, character development, and social commentary present in Harriet Beecher Stowe’s “Trials of a Housekeeper.” They encourage critical analysis and thoughtful reflection on the text’s portrayal of gender roles, social dynamics, and the experiences of housekeepers in the 19th century.
- How does Harriet Beecher Stowe depict the challenges and trials faced by housekeepers in “Trials of a Housekeeper”?
- Discuss the societal expectations placed on women in the 19th century, particularly in their roles as housekeepers. How does Stowe critique or challenge these expectations in her portrayal of the protagonist?
- Explore the theme of gender inequality in “Trials of a Housekeeper.” How does the text shed light on the limited opportunities and power dynamics faced by women during that time period?
- Analyze the character development of the housekeeper protagonist. How does she navigate and respond to the various trials and difficulties she encounters? What does her journey reveal about resilience and determination?
- Discuss the role of domestic work and the value attributed to it in “Trials of a Housekeeper.” How does Stowe challenge or reinforce societal attitudes towards domestic labor?
- Consider the relationship dynamics portrayed in the book, particularly between the housekeeper and the other characters. How do these relationships influence the housekeeper’s trials and experiences?
- Explore the themes of class and social status in “Trials of a Housekeeper.” How does Stowe depict the disparities between the housekeeper and those in higher social positions? What commentary does this provide on social hierarchies of the time?
- Discuss the significance of the title “Trials of a Housekeeper.” What do you think Stowe is trying to convey about the challenges faced by housekeepers and the importance of recognizing their work?
- Analyze Stowe’s writing style and use of literary techniques. How does her storytelling contribute to the portrayal of the housekeeper’s trials and the overall message of the narrative?
- Reflect on the relevance of “Trials of a Housekeeper” in contemporary society. What connections can be drawn between the experiences depicted in the book and the challenges faced by individuals in similar roles today?
Sources
Harriet Beecher Stowe Center. “Harriet Beecher Stowe Biography.” https://www.harrietbeecherstowecenter.org/harriet-beecher-stowe/harriet-beecher-stowe-life/
Hedrick, Joan D. Harriet Beecher Stowe: A Life. Oxford University Press, 1994.
Stowe, Harriet Beecher. The Writings of Harriet Beecher Stowe, Volume VIII, Public Domain.
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery and liberate slaves around the world.
A theme is a central topic, subject, or message within a narrative.